Diabetes is one of the most common medical conditions in the United States and worldwide, with as many as 1 in 10 adults diagnosed with diabetes at some point in their lives. For most people, the condition can be controlled by diet and lifestyle changes and medications, but others must monitor their blood sugar levels with finger pricks several times a day to manage their disease. If you or someone you know suffers from diabetes, these facts may help you better understand this potentially life-threatening condition.
1) There are three different types of diabetes
type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when your immune system attacks cells in your pancreas. These cells make up insulin, a hormone that helps move glucose out of your blood and into your body’s cells to be used as energy. With type 1 diabetes, you can’t produce any insulin at all, meaning that even small amounts of sugar or carbohydrates can lead to dangerously high blood sugar levels.
2) Some types are less serious than others
There are a few different types of diabetes. Type 1, which usually develops in children and young adults, results from an autoimmune disorder—basically, your body is attacking its own insulin-producing cells. Type 2 diabetes, as it’s called when it develops later in life (usually after age 40), is related to lifestyle factors like obesity and genetics; also known as adult-onset diabetes, it accounts for between 85 and 95 percent of cases. Gestational diabetes is a temporary form that occurs during pregnancy.
3) Type 1 is the most serious form

In both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, cells stop responding to insulin. But in people with Type 1 diabetes, their pancreas doesn’t produce any insulin at all—an autoimmune response causes beta cells to go haywire and attack their own bodies. In contrast, in someone with Type 2 diabetes, their body’s resistance to insulin—not a lack of production—is what causes high blood sugar levels.
4) Types 2 and 3 can be managed by diet
Type 2 diabetes is sometimes called adult-onset or lifestyle diabetes because it often develops as a result of poor diet and lack of exercise. In Type 2 diabetes, insulin is produced but not enough to manage blood sugar levels effectively. The exact cause of Type 2 diabetes is unknown, but genetics, family history and obesity are likely contributors.
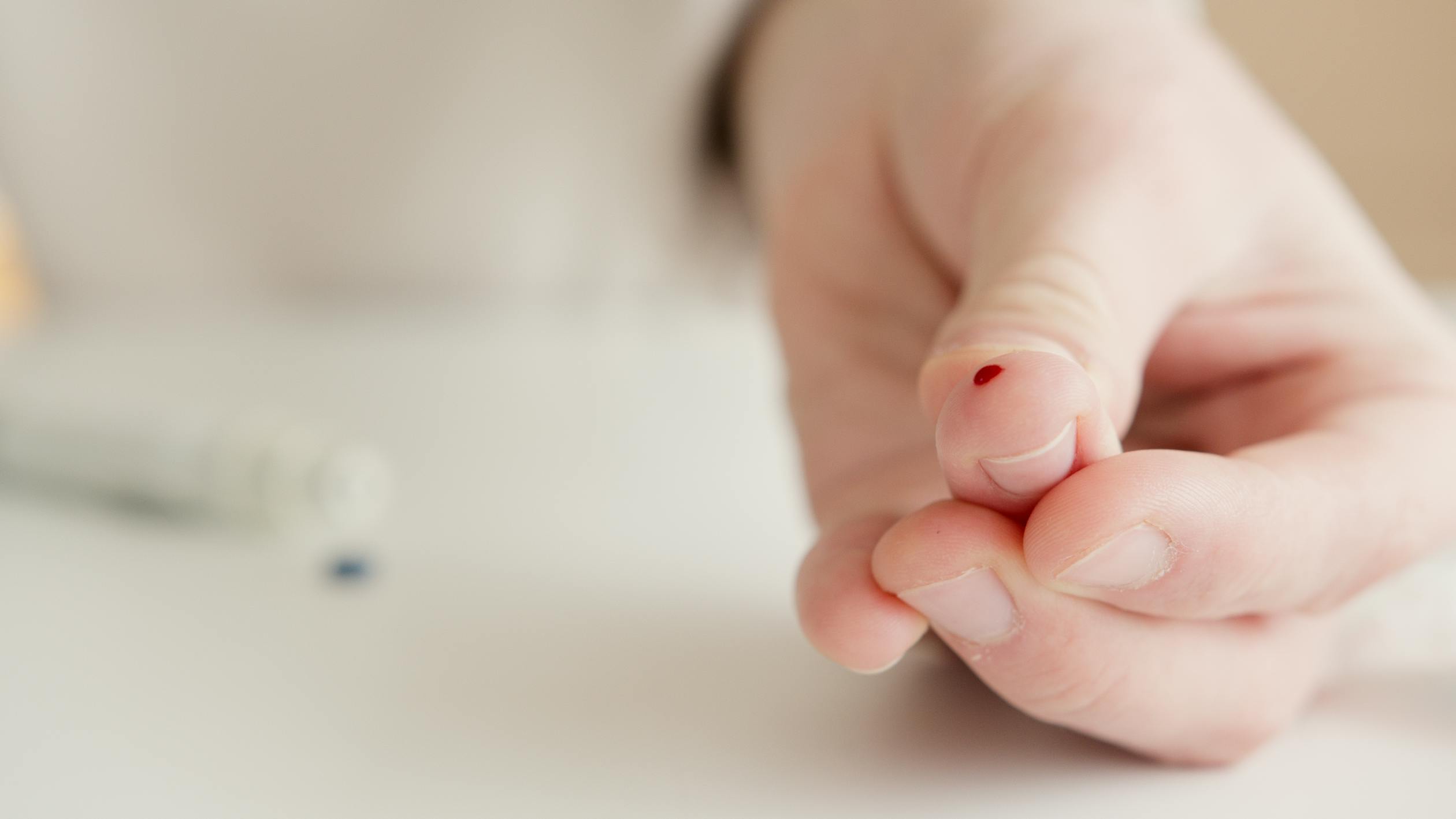
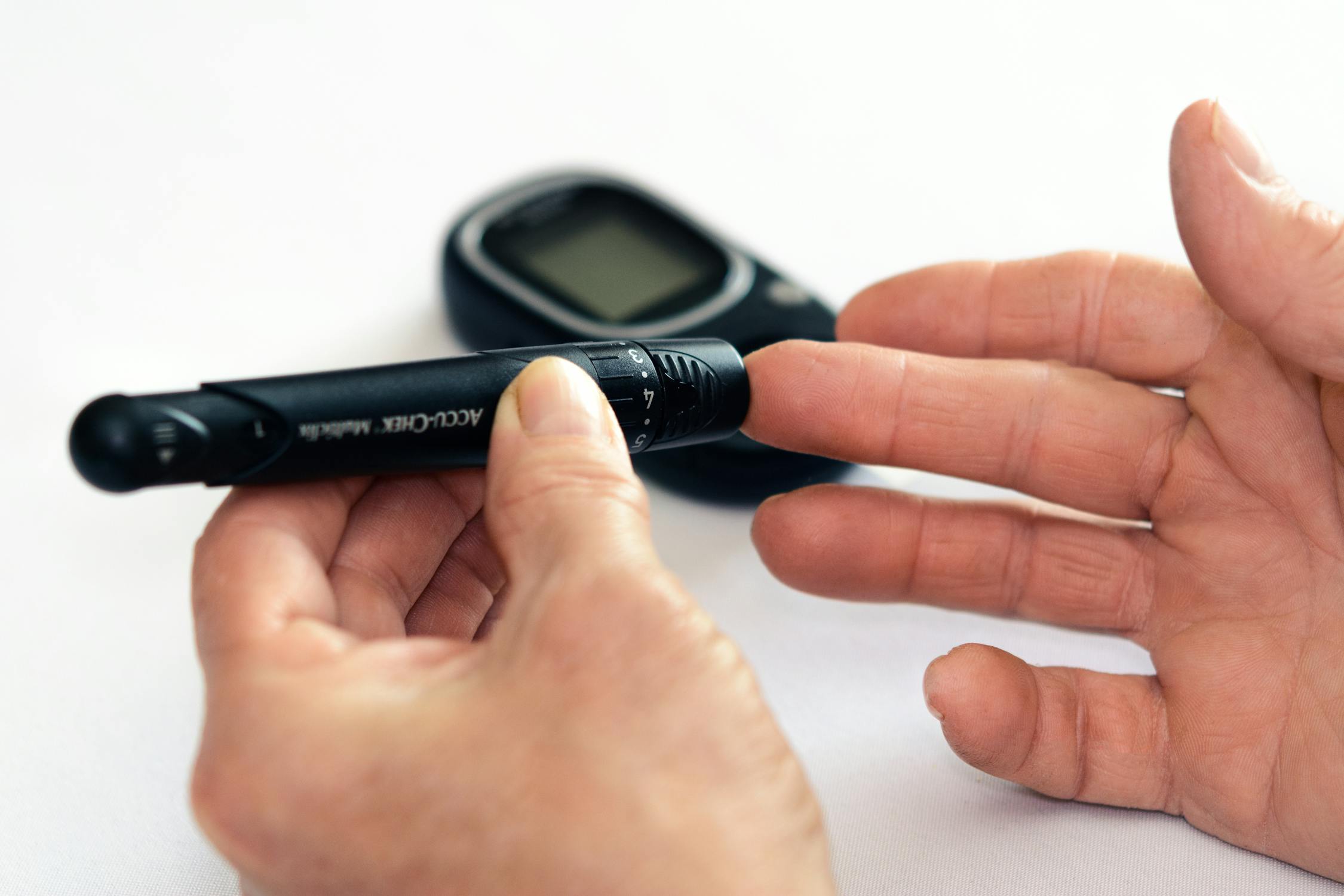
5) Diabetics must monitor their blood sugar levels regularly, preferably with a meter

Diabetics should constantly monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust insulin and meals accordingly. Some diabetics may want to measure their blood sugar at home (with an automatic or traditional meter), while others may prefer to visit a clinic or doctor’s office for testing. Regardless of your monitoring method, it’s important to know how diabetes affects your body and what you can do about it.
6) Blood sugar management involves eating right and exercising
Insulin, a hormone released by your pancreas, helps cells in your body absorb glucose. Glucose comes from carbohydrates you eat, and your blood glucose level rises after you eat foods with carbohydrates (also known as starches). Your blood glucose level becomes elevated when it’s too high for too long.
7) Diabetics also need to make sure they don’t get dehydrated or overheated

When you’re struggling to regulate your blood sugar levels, it can be hard to stay properly hydrated. Dehydration can lead to a whole host of complications for diabetics, from dry skin and fatigue to kidney damage and cognitive impairment. If you experience thirst or intense feelings of hunger that lead you to eat more food than usual, take note—you might have type 2 diabetes, which is one of many diseases that has dehydration as a side effect.
8) Diabetes affects more people than you think
Around 29 million people in America have diabetes, and 86 million more live with prediabetes, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. That’s why it’s important to learn as much as you can about diabetes—and make sure you know what symptoms to look out for. Here are ten things that people living with diabetes do every day, but many of us don’t even realize we’re doing.
9) Most diabetes cases can be managed through diet and exercise
Most diabetes cases can be managed through diet and exercise, but if you have Type 1 diabetes, you’ll need insulin shots or a pump to get your blood sugar levels under control. Properly monitoring your blood sugar levels is important in preventing future complications. A study in Diabetologia showed that people with Type 2 diabetes who maintained good glucose control were less likely to develop cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or kidney failure than those who did not keep their glucose under tight control.
10) Many diabetics live long, healthy lives
While diabetes is a serious disease, most people who have it can manage it so that it doesn’t affect their day-to-day life. And many people with diabetes live long and healthy lives, thanks to improved medication, technology, and care. In fact, according to recent statistics, approximately 94% of all diabetics will reach age 75.







